A Valuable Step in Cable Assembly & Wire Harness Manufacturing, Heat Shrinking Offers Enhanced Protection, Insulation & More
When manufacturing a precision electrical product like a cable assembly or wire harness, the goal is to ensure the final result is as effective, safe and durable as possible. Throughout a custom manufacturing project, engineers and technicians take a variety of beneficial steps to optimize the product for future use. Heat shrinking is one of them, offering several advantages from protecting sensitive splices to improving insulation.
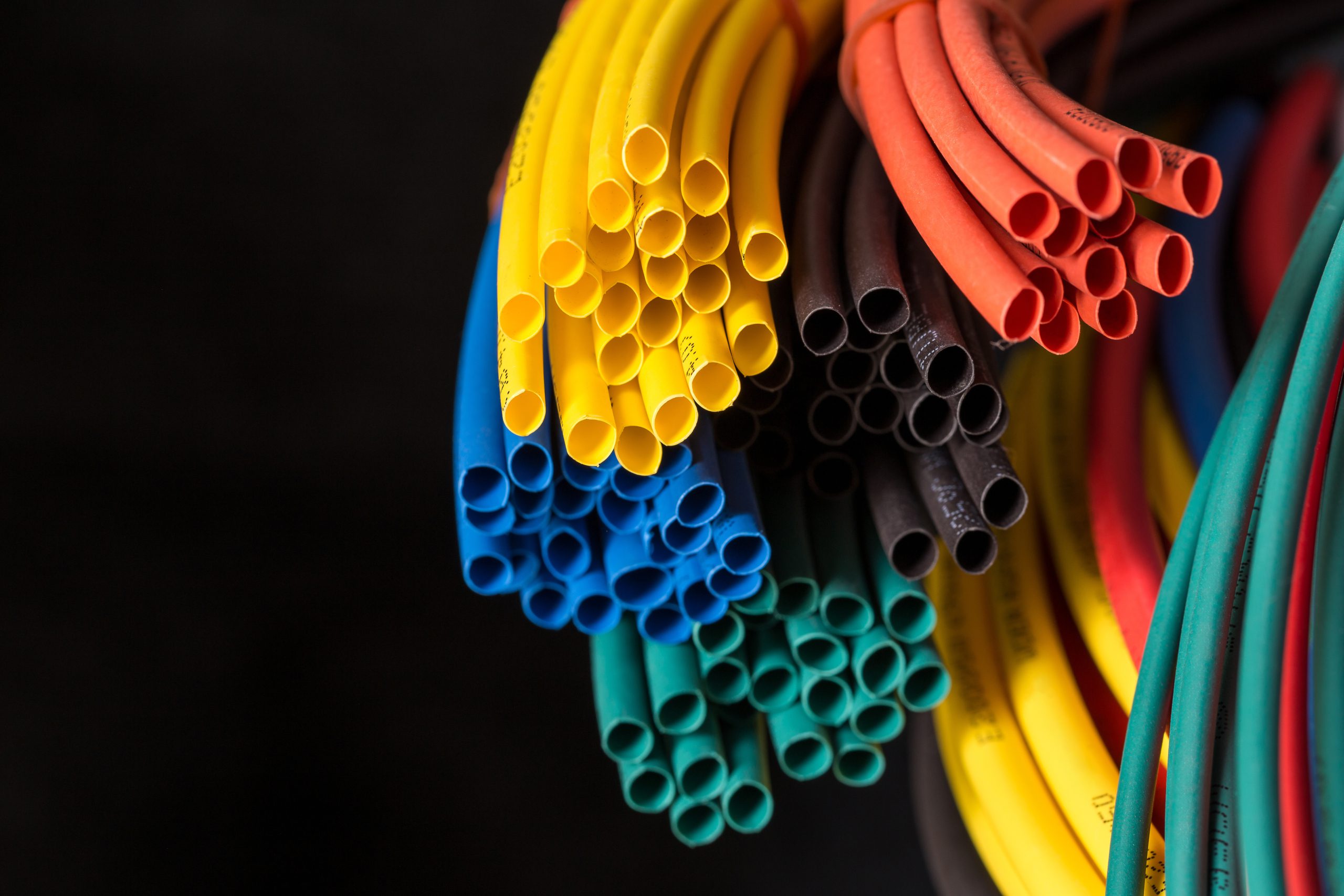
Heat shrink tubing, also called a heat shrink sleeve, is a versatile thermoplastic layer which is placed over a wire, cable, connection or component, then shrunk down via a heat gun, hot gas or other heat source. During heat shrinking, the tube material uniquely adheres to the contours of the object, shrinking radially instead of longitudinally, so the tube grows shorter and more compact in the process. This produces a tightly sealed fit and the benefits that come with it.
4 Key Benefits of Heat Shrink Tubing
1. Enhanced Protection
The most significant benefit of heat shrinking is its ability to help protect against threats to the transmission of data or power. It’s especially beneficial for products used in demanding environments like hospitals, factories and manufacturing plants.
Extreme temperatures, chemicals, UV light, moisture, and other external factors can damage the inner workings of a cable assembly, eventually leading to shorts and failures. With their airtight fit and unique material characteristics, heat shrink sleeves add an extra layer of protection for greater resilience.
2. Better Organization
Anyone familiar with complex electrical systems is familiar with cable spaghetti — the tangled mess of wires and cables that results from poor organization. Not only is it unattractive, but it can also lead to performance issues and make maintenance and integration more difficult.
Heat shrink tubing lets you bundle wires or cables into groups for easier management and a cleaner, more finished professional appearance. Additionally, tubing comes in a wide variety of colors and can be color-coded for easier identification and access.
3. Additional Insulation
If not properly insulated, some of the energy that flows through a cable assembly can seep out and adversely affect not only the cables’ performance but also their surrounding environment.
While wires and cables typically already feature some level of insulation, heat shrink tubing helps further insulate conductors, especially at vulnerable splice and connection points, to prevent the loss and dissipation of energy and maintain signal integrity. Additionally, it provides another level of safety, guarding against dangers like electrical shock. Tubing can also complement cable shielding in efforts to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues.
4. Less Cable Stress
Cables and wires can undergo a high degree of stress from frequent stretching and bending which can lead to performance issues and even failure over time. Heat shrinking enhances mechanical support which reduces strain on wires, components, and connectors. This helps slow down the wear and tear, and increases the lifespan of assemblies and harnesses.
The technician experts at CAI have been manufacturing cable assemblies and wire harnesses for over 35 years, consistently meeting and exceeding industry standards and customer expectations. For more on heat shrinking and how it can improve your custom electrical project, contact CAI today.
Heat Shrink Tube Materials & Types
To fully realize the benefits of heat shrinking, you have to make sure you have the right tubing for your specific application. There are a number of different tubing materials, each with its own unique properties and advantages, giving you plenty of options.
The most popular heat shrink material, especially for military, aerospace, and railway applications, is polyolefin, a flexible, lightweight synthetic polymer highly resistant to chemicals and extreme heat. Adhesive-lined polyolefin has an inner liner that melts and adheres to what’s inside, for a more secure fit.
Typically less expensive than other tubing materials, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is another versatile choice, featuring an abrasion-resistant flat surface which takes colors well and can be used outdoors with a UV stabilizer.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), better known as Teflon, is a synthetic compound with a small coefficient of friction so substances slide off it easily, making it highly resistant to chemicals and punctures. Other heat shrink materials include elastomeric, FEP, PVDF, silicone, Viton and more.
When it comes to the level of protection needed, there are two wall types of heat shrink tubing: Thin (or single) wall, and dual (or double) wall. Featuring more reliable consistency and physical properties than double wall types, single wall tubing delivers all the benefits mentioned above. For applications in which corrosion resistance is a top priority, double wall tubing features an extra layer of adhesive for a stronger moisture-resistant seal.
For all your heat shrinking, cable assembly and wire harness needs, CAI will work with you to make sure your vision is fully realized — from prototype to production. For expert guidance and manufacturing solutions you can count on, reach out to CAI today.